Main Types:
1.Switching Diodes(VRRM:20V~600V/IO:0.1A~1A)
These diodes have the ability to switch on (conduct current) when a positive voltage is applied (ON) and switch off (no current flow) when a reverse voltage is applied (OFF). They exhibit excellent switching characteristics, with short reverse recovery time (trr) compared to other diodes. trr refers to the time it takes for a switching diode to transition from the conducting state to fully closed state. After turning off, electrons cannot instantly stop, resulting in some reverse current flow. The greater the leakage current, the higher the losses.
2.Zener Diodes(VZ:3.3V~110V/0.2W~1W)
Zener diodes operate in the reverse breakdown region, where current changes significantly while the voltage remains relatively constant. They play a stabilizing role in circuits by maintaining a consistent voltage. Zener breakdown is reversible; once the reverse voltage is removed, the Zener diode returns to normal operation. As long as the reverse current stays within the allowed maximum range, the Zener diode won’t experience thermal breakdown. Zener diodes can be categorized as either Zener breakdown (for voltages below 6V, with a negative temperature coefficient) or avalanche breakdown (for voltages above 6V, with a positive temperature coefficient).
3.Schottky Diodes(VRRM:20V~200V/IO:0.07A~50A/VF:0.33V~1.05V)
Schottky barrier diodes utilize the metal-semiconductor junction (Schottky barrier) to exhibit unique characteristics. Compared to regular PN junction diodes, Schottky diodes have lower forward voltage drop, faster switching speed, but higher reverse leakage current and lower reverse voltage tolerance. They find applications in high-frequency, low-voltage, and high-current rectification, as well as reverse polarity protection.
4.Rectifier Diodes and Bridge Rectifiers(VRRM:20V~1000V/IF05A~120A)
Rectifier diodes are used for converting AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current). They handle high voltage and current. Bridge rectifiers consist of four rectifier diodes internally and perform full-wave rectification. Both are commonly used in low-frequency half-wave rectifier circuits.
5.Fast Recovery Diodes(VRRM:50V~1200V/IO1A~60A/Trr:20ns~500ns)
Fast recovery diodes are semiconductor diodes with excellent switching characteristics, short reverse recovery time, and high reverse breakdown voltage. They are used in electronic circuits such as switch-mode power supplies, PWM (pulse-width modulation) controllers, and inverters. They serve as high-frequency rectifiers, freewheeling diodes, or snubber diodes. These diodes can be classified into fast recovery and ultra-fast recovery based on their performance. The former has a reverse recovery time in the hundreds of nanoseconds or longer, while the latter is below 100 nanoseconds.
6.ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) Diodes(VRWM:3V~24V/IPPM:1A~40A/PPP:8W~400W/CJ:0.15PF~65PF)
ESD diodes are transient voltage suppressors that respond extremely quickly (picoseconds) and have very low junction capacitance. They protect devices and circuits from various static electricity-related damage.
7.TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) Diodes(VRWM:5V~440V/IPPM:0.5A~320A/PPP:200W~3000W)
TVS diodes are designed to absorb high transient energy during reverse breakdown of the PN junction while clamping the voltage to a lower level. They are widely used as efficient circuit protection devices, with ultra-fast response times (subnanoseconds) and high surge absorption capacity.

SOD-123

SOD-123FL
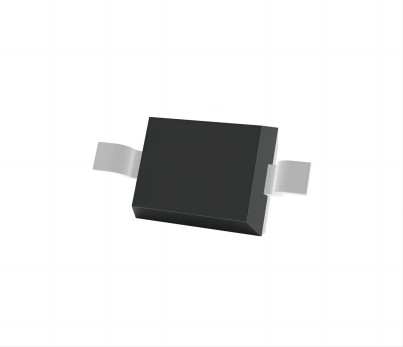
SOD-323
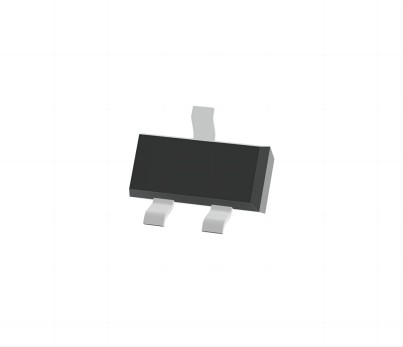
SOT-23
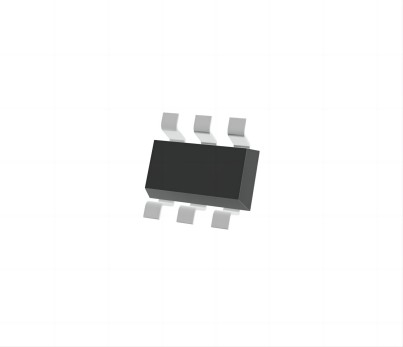
SOT23-6
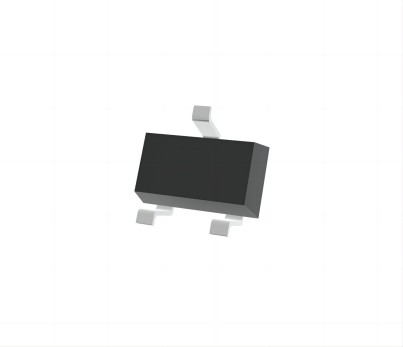
SOT-323
SOT-363
SOT-523

TO-220F

TO-220

TO-252
TO-251
TO-263
TO-262
TO-277
QQ:
手机:0086-136 0286 9588
电话: 0086-20-2262-5106
邮箱: tina.dai@lettersemi.com
地址:RM708 Innovation Building,Tian An Technology Park, Ying Bin Road, Panyu Zone, Guangzhou City,China